Web services are application modules executed by a web server, allowing the exchange of data and execution of code in the context of the web server.
Web services allow an easy implementation for remote calls to available application modules. This allows an application to move its user interface from being coupled with the processing code towards the end-userís machine.
More information can be found at http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms950421.aspx
How do web services work?
The web services implemented in Content Studio supports, in addition to the usual soap protocol, also querystrings (http-method get) and post-data (http-method post). While the soap protocol uses the post method, the data format used is different and is as such handled by a different protocol handler.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Soap |
This is the default web service protocol in asp.net. This protocol will be used
when coding against an web service using the normal Visual Studio behavior. More information: http://www.w3.org/TR/soap/ |
| HttpGet |
Sends any method parameters as normal querystring data. (key=value&key=value&...) Example: [path]/ContentStudio_CSApplication.asmx/SiteList_818683A4?NewSyntax=true |
| HttpPost |
Sends any method parameters as normal post data. (key=value&key=value&...) This is the method used when accessing the web service directly in your webbrowser and invoking it. |
NOTE: Notice that HttpGet and HttpPost only handle parameters of basic types that is not marked as out or ref. Also, HttpGet and HttpPost only handles return results of basic type. Any attempt to call methods that has an invalid parameter or return type will fail.
Web services in Content Studio
Installing the web services support under Content Studio will make them available for all sites hosted under that instance of Content Studio.
Web services in Content Studio will be installed under /[admin-web]/webservices/ where they can be accessed with any capable client.
All web services are named after their backend class, replacing any dots with underscores. See table below for example of naming system in use.
| Example class | Web service filename |
|---|---|
| ContentStudio.CSApplication | ContentStudio_CSApplication.asmx |
| ContentStudio.Document.EPT.EPT | ContentStudio_Document_EPT_EPT.asmx |
| ContentStudio.Security.SessionManager | ContentStudio_Security_SessionManager.asmx |
NOTE: For a complete list of API classes exposed as Web Services, see the Available Web Services article in this documentation.
Web services in Content Studio implements pseudo-overloading by changing the MessageName that identifies every method to a document unique identifier. This is done by taking the method name and appending a hash created from the method declaration. This can be ignored when using web services with Visual Studio since Visual Studio automaticly handles the the serialization over the soap protocol, and provides a proxy class with proper overloading and parameters.
Sessions in Content Studio
Many web services in Content Studio uses an SessionID of integer value to identify the current user. A SessionID can be aquired by calling the OpenSession(int ConnectionID) method on ContentStudio.Security.SessionManager (/[path]/ContentStudio_Security_SessionManager.asmx/OpenSession_E7DAF8BD?ConnectionID=#). For more documentation regarding how Content Studio uses sessions, see the Content Studio 5 API Documentation.
Implementing web services in Visual Studio 2005
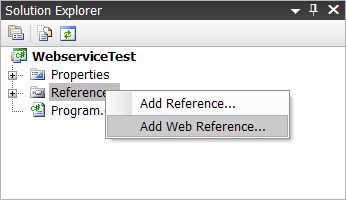
- Add a web reference
Right click on the References node, and choose Add Web Reference.
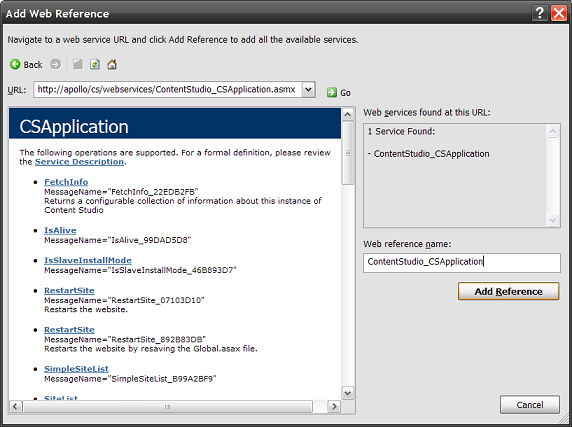
- Specify location of web service
Write the location to the web service you want to use in the topmost address bar. For easy remembering; change your web reference name in the lower right textbox to the filename of the web service.
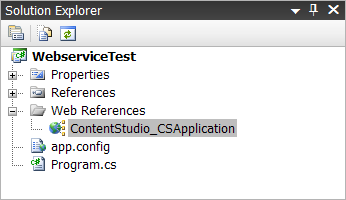
- Verify web service
Your solution explorer should now contain the web reference you just added.
- Call a web service method
Content Studio requires authentication before allowing access to any web services. This is done by the example code above by setting the Credentials property of your initialized web service instance to System.Net.CredentialCache.DefaultNetworkCredentials. The web server will return a 401 Unauthorized if this isnít done before executing any method on the web service instance.
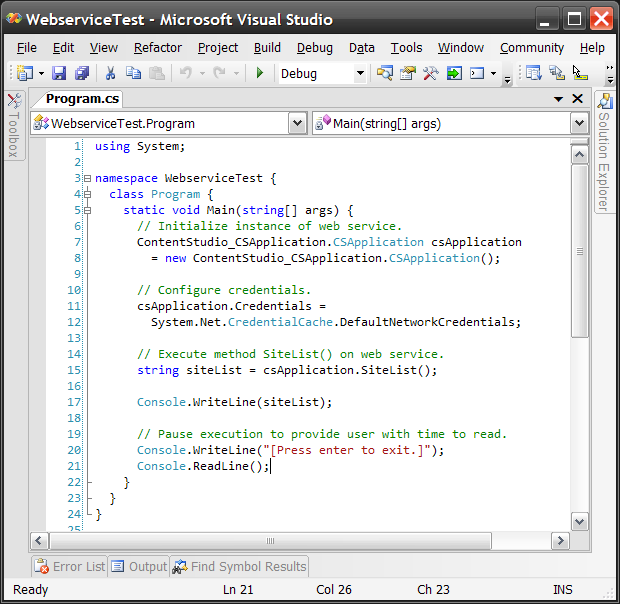
C#VB.NETusing System; namespace WebserviceTest { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ContentStudio_CSApplication.CSApplication csApplication = new ContentStudio_CSApplication.CSApplication(); // Configure credentials. csApplication.Credentials = System.Net.CredentialCache.DefaultNetworkCredentials; // Execute method SiteList() on web service. string siteList = csApplication.SiteList(); Console.WriteLine(siteList); // Pause execution to provide user with time to read. Console.WriteLine("[Press enter to exit.]"); Console.ReadLine(); } } }Imports System Namespace WebserviceTest Class Program Public Shared Sub Main(args() As String) Dim csApplication As New ContentStudio_CSApplication.CSApplication() ' Configure credentials. csApplication.Credentials = _ System.Net.CredentialCache.DefaultNetworkCredentials ' Execute method SiteList() on web service. Dim siteList As String = csApplication.SiteList() Console.WriteLine(siteList) ' Pause execution to provide user with time to read. Console.WriteLine("[Press enter to exit.]") Console.ReadLine() End Sub End Class End Namespace